Global capital markets players can be divided into three core categories: (i) buy-side firms, (ii) sell-side firms and (iii) financial intermediaries. Essentially, buy-side firms are those who buy investment securities mainly for fund management purpose. On the other end, sell-side firms are involved in the creation, promotion and sale of traded securities to the public market. Financial intermediaries are the middlemen who assist to facilitate the financial transactions between two parties. Let’s dive deeper into the buy-side of the capital markets that covers the following areas: (i) hedge funds, (ii) private equity and (iii) venture capital.
About Hedge Funds
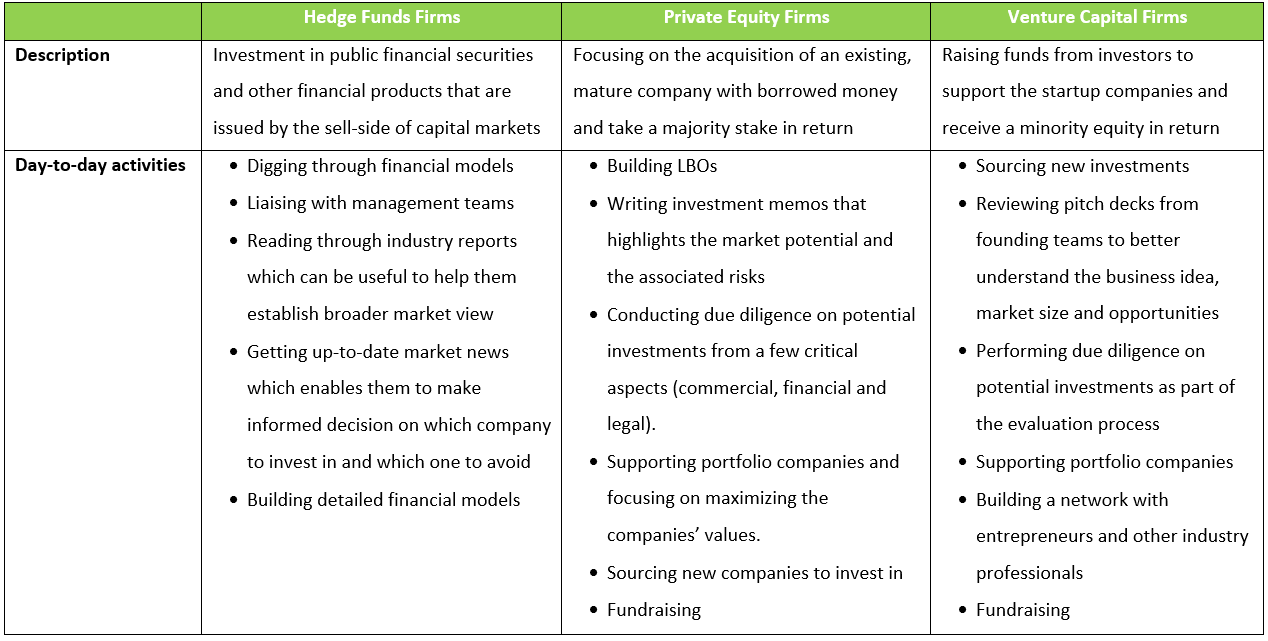
Hedge funds focus on pooling money primarily from accredited investors and investing it in public financial securities such as stocks, fixed income assets, commodities and so on. There are various strategies that hedge fund managers will employ to generate better returns for their investors and reduce their risk exposure. This includes long/short equity, event-driven and market arbitrage to name a few. The fund managers will invest in different securities and equities that match the said strategy in order to maximise the returns despite market fluctuations.
Read More: How to start a hedge fund in Singapore
About Private Equity
On the other hand, private equity (PE) firms tend to focus more on leveraged buyout transactions (LBOs). A leveraged buyout refers to the acquisition of an existing company by a PE firm using a relatively large portion of outside debt financing while the balance is funded with their own equity. The PE firm will then make operational improvements to the company and help to improve its financial health by paying off as much debt as possible using company’s cash flows. When the company’s valuation is getting higher and the timing is right, the PE firm will exit the investment through initial public offerings (IPOs) or sell the portfolio company to interested party. The exit of investment often takes place between three to seven years after the initial investment.
About Venture Capital
A venture capital is a form of private equity that investors provide to fund the startup companies in their early stage with long-term growth potential. They will receive a minority equity (50% or less) in return. In addition, venture capital investors will help entrepreneurs to build their businesses from the ground up based on their strong knowledge of the financial markets and diversified social circles. In the decision-making process, venture capitalists will first assess the company based on their growth potential, management team and the competitive advantage of the product or service. It is a high-risk high-reward industry and the venture capitalists who are risk takers shall expect the returns to come 7 to 10 years later.
The following table shows the differences of hedge funds, private equity and venture capital: